Health Tip - Chronic Pain




Chronic Pain maybe related to:

We are going to start a series on combating Chronic Pain using Alternative Treatments from Acupuncture to Marijuana.


Controlling Chronic Pain is not easy but through research and collaboration with your doctor you can find relief. You may have to integrate an alternative treatment with your pain management plan.
You can become Pain Free!
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~



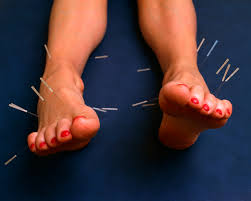
The most thoroughly studied mechanism of stimulation of Acupuncture points employs penetration of the skin by thin, solid, metallic needles, which are manipulated manually or by electrical stimulation.
What is Chronic Pain?
Chronic Pain: Pain (an unpleasant sense of discomfort) that persists or progresses over a long period of time.
There are two types of Chronic Pain:
- Acute Pain arises suddenly in response to a specific injury and is usually treatable.
- Chronic Pain persists over time and is often resistant to medical treatments. Chronic pain is pain that has lasted for a long time.
Chronic Pain maybe related to:
- Diabetes
- Arthritis
- Back injuries
- Migraine
- Fibromyalgia
- Osteoarthritis
- Cancer
- Shingles
- Sciatica
- Trauma
- Sports injuries
Chronic Pain may worsen in response to environmental or psychological factors.
Traditional treatment for Chronic Pain is medication and surgery.
We are going to start a series on combating Chronic Pain using Alternative Treatments from Acupuncture to Marijuana.
Controlling Chronic Pain is not easy but through research and collaboration with your doctor you can find relief. You may have to integrate an alternative treatment with your pain management plan.
You can become Pain Free!
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Our first alternative treatment for Chronic Pain is Acupuncture.
Acupuncture originates from China and has been practiced there for thousands of years.
Acupuncture originates from China and has been practiced there for thousands of years.
Acupuncture is the practice of inserting needles into the body to reduce pain. Acupuncture is a series of procedures involving the stimulation of anatomical locations on or in the skin by a variety of techniques.
Acupuncture generally involves several weekly or nightly treatments. Most course consist of up to 12 sessions.
A visit to an Acupuncturist will involve an exam and an assessment of your condition, the insertion of needles and advice on self-care.
Most session will last up to 1 hour or may go longer.
You may be asked to sit in a chair, lie down, either face-up, face-down, or on your side. As each needle is inserted you may feel them, initially without pain. However, when the needle reaches the right depth there maybe a deep aching sensation.
Acupuncture generally involves several weekly or nightly treatments. Most course consist of up to 12 sessions.
A visit to an Acupuncturist will involve an exam and an assessment of your condition, the insertion of needles and advice on self-care.
Most session will last up to 1 hour or may go longer.
You may be asked to sit in a chair, lie down, either face-up, face-down, or on your side. As each needle is inserted you may feel them, initially without pain. However, when the needle reaches the right depth there maybe a deep aching sensation.
There are different approaches to diagnosis and treatment in Acupuncture. The American Acupuncture incorporates medical traditions from China, Japan, Korea, and other countries.
In Western societies Acupuncture is explained including concepts of neuroscience, as places where nerves, muscles and connective tissue can be stimulated. Western practitioners say that stimulation increases blood flow while at the same time triggering the activity of our own body's natural painkillers.
In Western societies Acupuncture is explained including concepts of neuroscience, as places where nerves, muscles and connective tissue can be stimulated. Western practitioners say that stimulation increases blood flow while at the same time triggering the activity of our own body's natural painkillers.
How Does It Work?
According to WHO (World Health Organization) Acupuncture is effective for treating 28 conditions, while evidence indicates it may have an effective therapeutic value for many more.
Conditions Treated with Acupuncture:
- Neck or Cervical Pain
- Shoulder Pain
- Lower Back Pain
- Sciatica
- Hip Pain
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Headaches & Migraines
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Sinus Problems
- Arthritis & Arthritic Pain
- Jaw and Face Pain
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Tennis and Golfer's Elbow
- Sports Injuries
- Motor Vehicle Injuries
- Bladder Infection
- Stress Related Disorders
- Menstrual & PMS Problems
- Smoking Addiction
- Obesity & Overweight
- Infertility
What are the Benefits of Acupuncture?
- When performed correctly it is safe;
- There are very few side effects;
- An effective combination treatment;
- Effective in controlling some types of pain;
- An alternative to persons who do not respond to pain medications;
- An alternative for patients who do not want to take pain medications;
- Improved health and quality of life;
- Stress reduction;
- Pain reduction;
- Emotional balance;
- Insomnia relief;
- Strengthening your immune system;
- Reduction of side effects of Chemo and Radiation Therapies
What are the Risks of Acupuncture?
- May cause bleeding, bruising and soreness at the insertion sites;
- A deep insertion in the Thorax maybe harmful for internal organs (very rare);
- If inserted deeply into the chest or upper back there is a risk of collapsed lung (very rare).
Remember!
To always go to a licensed Acupuncturist and make sure that they use sterile single use disposable needles.
Special Note: if you have a bleeding disorder or taking blood thinners please consult your doctor before starting this treatment.
Information is Power!
Have an open mind
lets break the cycle of Chronic Pain
lets break the cycle of Chronic Pain
For more information go to www.WebMd.com, www.medicalnewstoday.com, www.mdguidelines.com, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, www.uptodate.com, www.amcollege.edu/benefitsacupuncture, www.iasp-pain.org, www.emedicinehealth.com, or www.medicinenet.
Next week - Acupressure and Aromatherapy
Live Well
Doc V




No comments:
Post a Comment